|
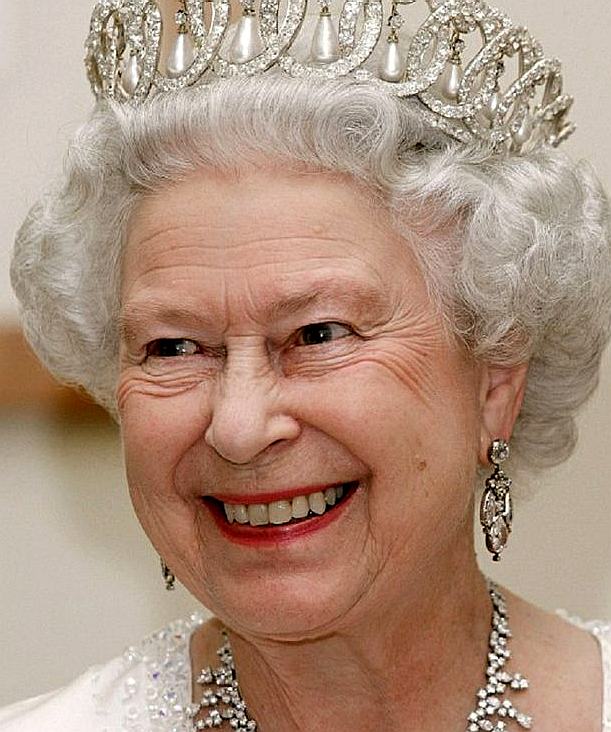
H. M. QUEEN ELIZABETH II
Please use our A-Z INDEX to navigate this site or return HOME
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
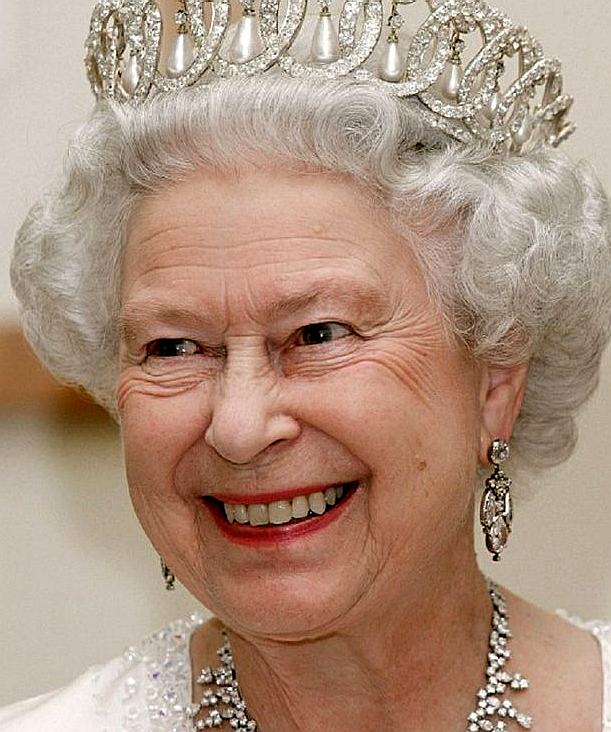
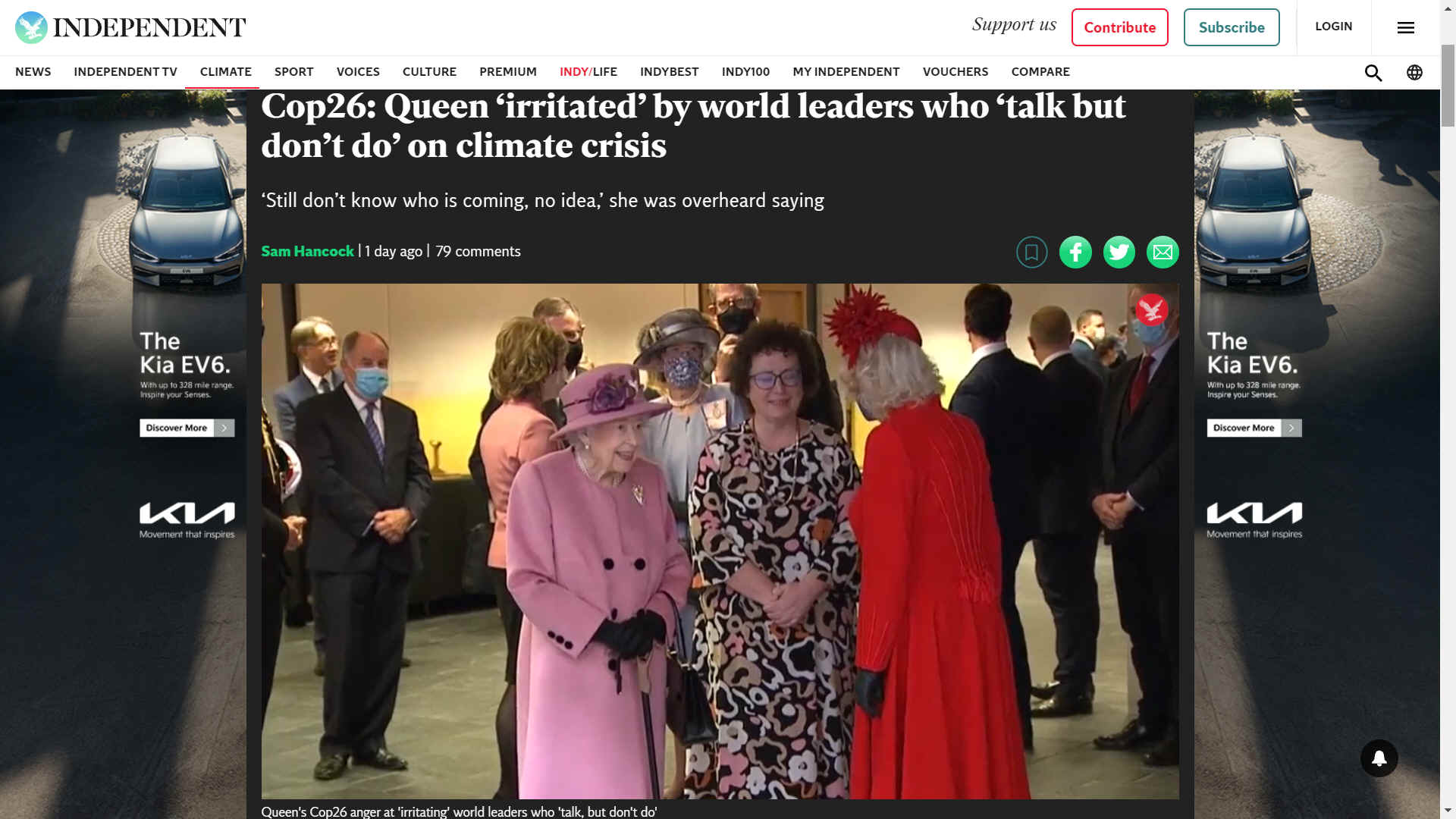
Her Majesty, Queen Elizabeth
COP
26 - OCTOBER 2021 - THE INDEPENDENT
- QUEEN IRRITATED BY TALKERS
SHIPS NAMED AFTER QUEEN ELIZABETH
Not unsurprisingly, there are a number of vessels that bear the name: "Queen Elizabeth." There are three Cunard liners: RMS Queen Elizabeth, Queen Elizabeth 2 (QE2) and MS Queen Elizabeth (QE), a nuclear powered aircraft carrier, HMS Queen Elizabeth (RO8), HMS Queen Elizabeth a dreadnought class battleship, and a solar powered Canadian canal boat.
Of these in pollution terms, the canal boat is a shining star. The most polluting is the RO8, because of the dumping of spent nuclear material in the oceans.
ABOUT THE QUEEN
Great Britain, or the United Kingdom, is a Constitutional Monarchy ruled by Queen Elizabeth Windsor at the time of writing.
She is the second Queen to bear the name Elizabeth, after Good Queen Bess in 1558.
She is head of the British Royal Family, has 4 children, 8 grandchildren and 7 great-grandchildren.
Queen Elizabeth II became Queen of the United Kingdom and Head of the Commonwealth on 6th February 1952.
She is the 32nd great-granddaughter of King Alfred the Great who was the first effective King of England
(871-899).
Queen Elizabeth married the Duke of Edinburgh on 20 November 1947 at Westminster Abbey in London.
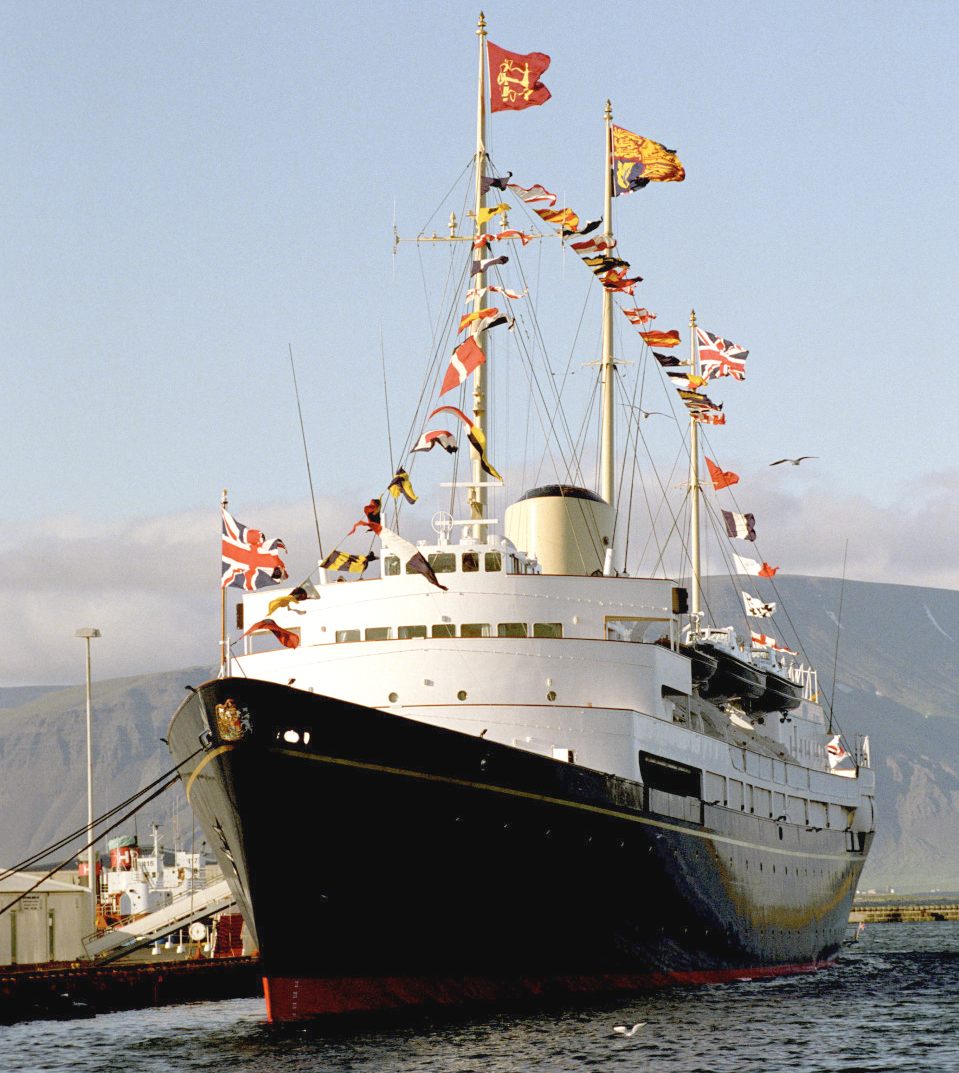
The Royal Yacht Britannia was decommissioned on 11 December 1997, causing the Queen to shed a tear in public.
On 21st December 2007 she became the oldest reigning British monarch having lived longer than Queen Victoria who died 22nd January 1901 aged 81 years, 7 months and 29 days.
In 2012 Queen Elizabeth II celebrated the
Diamond 60th Jubilee of her
reign. The 2nd June 2013 was the 60th anniversary of her coronation. On 20th November 2012 Queen Elizabeth II celebrated her 65th wedding anniversary.
On 21st April 2018
the Queen became 92 years old.
In April 2021, the Queen will be 95 years old. Long live the Queen.
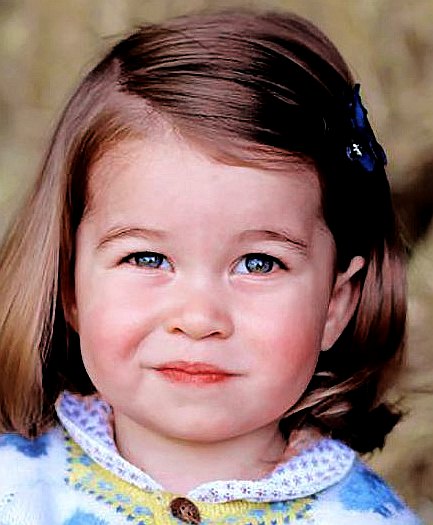
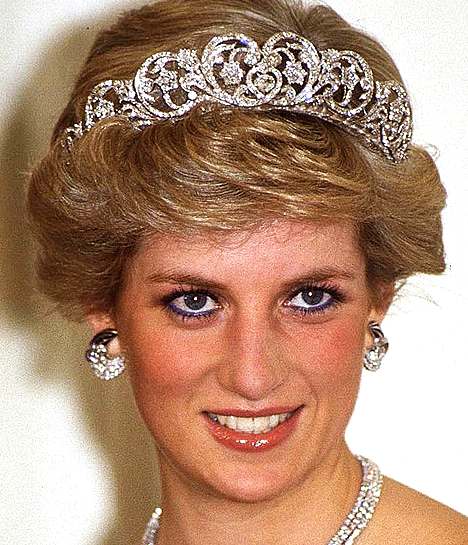
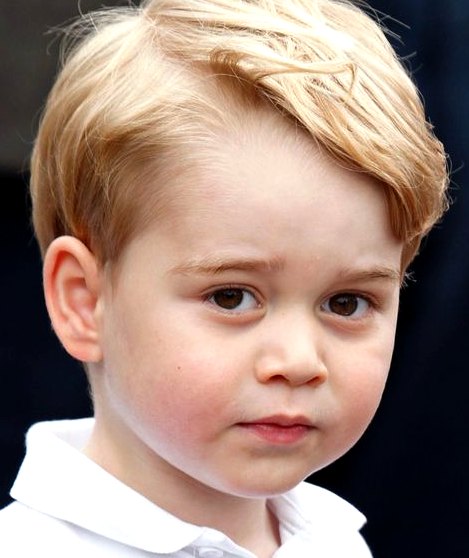
ROYALS GALLERY 2018
ENGLAND'S MARITIME HERITAGE IN BRIEF
England became a sea power of note with the help of privateers, known as Sea Dogs, essentially, pirates that sailed during the Privateering Era under the leadership of Queen Elizabeth I between 1560 and 1605.
During this time they had explicit permission from 'Good Queen Bess,' known as a Letter of Marque, which allowed them to engage in acts of piracy against the Spanish and other colonial powers the English were at war with at the time.
This custom continued into the Buccaneering era with King Charles II until by 1725 under King George I, the British Royal Navy virtually eliminated rogue (pirate) captains who failed to surrender under amnesty, such as with the execution of Captain William Kidd.
Other great exploits were against the French in 1805, such as the Battle of Trafalgar during which Admiral Horatio Nelson was shot aboard HMS Victory. For some years after with HMS Warrior (1860) Britain almost literally ruled the waves, until World War One, when technology accelerated naval development significantly.
Since the Second World War, British sea-power gave way to globalization and the US, Russian and Chinese super-powers.
The UK maintains nuclear powered submarines (Astute) and aircraft carriers, and is thus a contributor to nuclear waste, seen as necessary to keep peace, but the reverse of what the International Maritime Organization are striving for by 2100: zero emissions.
The Elizabeth Swann represents a move to cleaner ocean transport, now demanding low sulfur diesel fuels. Electric, solar and wind powered shipping could be the pinnacle of environmental achievement in years to come - if it comes to pass. Though, hydrogen fuel cells for cargo ships may play a significant part in the IMO's plans.
Please use our A-Z INDEX to navigate this site
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This website is Copyright © 2021 Jameson Hunter Ltd
|