|
FROM THE EARTH TO THE MOON
Please use our A-Z INDEX to navigate this site or return HOME
|
|
Jules Verne has always been considered as an author ahead of the times and this book in particular shows you exactly why. Even though the book may at times seem implausible the fact remains that Verne did manage to get some of the information right from the overall cost of such a trip to some of the effects that a traveler may face when traveling to the moon. This is Verne at his creative best and one of the reasons why so many of his novels are still ranked among the top 10 of Jules Verne books.
Best
known for '20,000
Leagues Under the Sea' and Around
The World In Eighty Days, Jules Verne also authored a number of
other popular novels, that made it onto the big screen, such as 'The
Mysterious Island,' and 'Journey To The Centre Of The World.'
From the earth to the moon, tells us that man has dreamed of what it would be like to visit our tide giving counterbalance. Jules Verne has always been considered as an author ahead of the times and this book in particular shows you exactly why. Even though the book may at times seem implausible the fact remains that Verne did manage to get some of the information right from the overall cost of such a trip to some of the effects that a traveler may face when traveling to the moon. This is Verne at his creative best and one of the reasons why so many of his novels are still ranked so highly.
PLOT
The story opens some time after the end of the American Civil War. The Baltimore Gun Club, a society dedicated to the design of weapons of all kinds (especially cannons), comes together when Impey Barbicane, its president, calls them to support his latest idea. He's done some calculations, and believes that they could construct a cannon capable of shooting a projectile to the Moon. After receiving the support of his companions, another meeting is held to decide the place from which the projectile will be fired, the dimensions and materials of both the cannon and the projectile, and which kind of powder they are to use.
IN POPULAR CULTURE
The novel was adapted as the opera Le voyage dans la lune in 1875, with music by Jacques Offenbach.
From the Earth to the Moon: A Direct Route in 97 Hours, 20 Minutes (French: De la Terre à la Lune, trajet direct en 97 heures 20 minutes) is an 1865 novel by Jules Verne. It tells the story of the Baltimore Gun Club, a post-American Civil War society of weapons enthusiasts, and their attempts to build an enormous Columbiad space gun and launch three people—the Gun Club's president, his Philadelphian armor-making rival, and a French poet—in a projectile with the goal of a Moon landing. Five years later, Verne wrote a sequel called Around the Moon.
Jules Verne was the author of many adventure stories:
1
Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea
9
Round the Moon (Extraordinary Voyages, #7)
Jules Verne is also known as the Father of Science Fiction
|
|
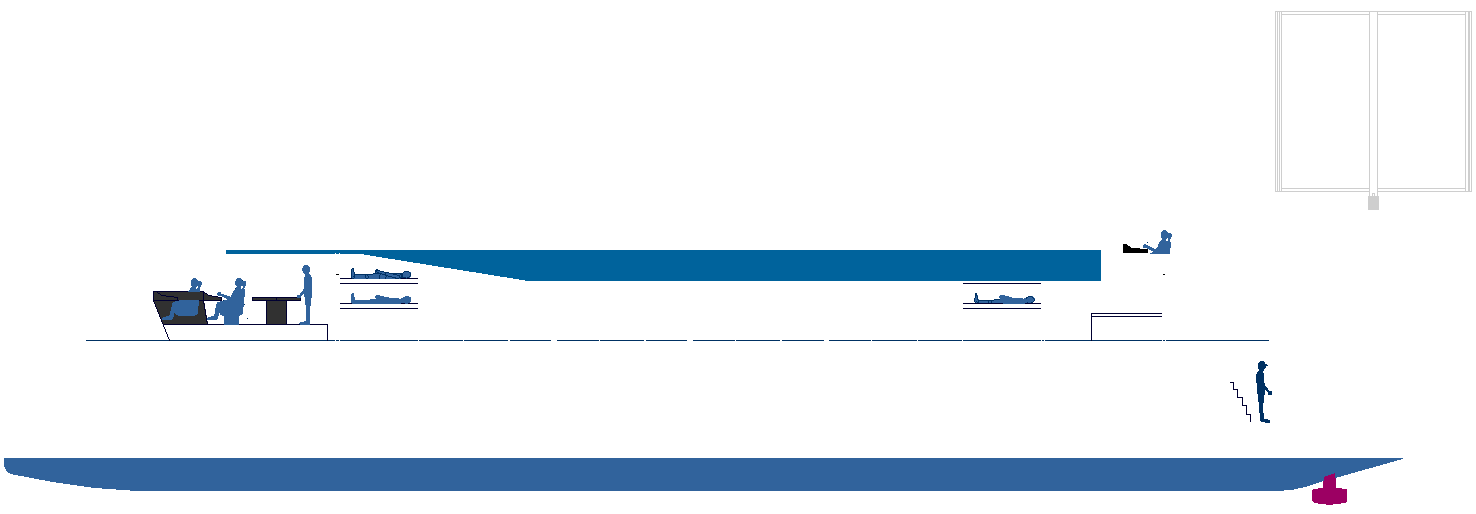
ZEWT ALORS - The solar and wind powered 'Elizabeth Swann' will feature solar collectors and wind energy harvesting apparatus in an advanced configuration. Her hull configuration is ideal for mass hydrogen storage tanks, offering ranges of up to 4,000nm on compressed gas, and could circumnavigate the globe on one fill up of liquid hydrogen, stored in two cryogenic tanks. Unfortunately, at this stage not in under 80 days, to equal the famous Jules Verne round the world record.
|
|
It was Jules Verne's fictional character, 'Philleas Fogg', who suggested that it might be possible to travel Around The World In 80 Days. But what about doing it in a Zero Emission yacht driven by electric hydro-jets? With the advent of solar power and liquid hydrogen, it is a distinct possibility - on a scale of the wager that the legendary Philleas Fogg entered into at the Reform Club in 1872.
In 1874, Jules Verne set out a prescient vision that has inspired governments and entrepreneurs in the 147 years since. In his book The Mysterious Island, Verne wrote of a world where "water will one day be employed as fuel, that hydrogen and oxygen which constitute it, used singly or together, will furnish an inexhaustible source of heat and light, of an intensity of which coal is not capable."
In 2021 we have the technology to make that foretelling a reality, to include using hydrogen to travel around the world in 80 days.
JULES VERNE LINKS & REFERENCE
http://jules-verne.org/
|
|
Please use our A-Z INDEX to navigate this site or return HOME
This website is Copyright © 2021 Jameson Hunter Ltd
|